Motorcycle safety relies on being seen by others.
Motorcycles are often overlooked in traffic. Accident analysis shows that in more than half of cases, collisions with motorcycles are caused by the other vehicle driver. And not seeing the motorcycling coming, or misjudging distance and speed, are primary causes. “I never saw the bike” is a typical explanation of the driver.
By making motorcycles part of Vehicle-to-Vehicle communication systems, advance information or warnings could be given in case of critical situations.
By making motorcycles part of Vehicle-to-Vehicle communication systems, advance information or warnings could be given in case of critical situations.
Connectivity has great potential.
Wireless communication between vehicles (and infrastructure) will help to detect dangerous situations earlier than the human eye can see.
This Cooperative Intelligent Transport System (C-ITS) has been initiated by car makers to improve driving safety. A promising technology to make sure, that other vehicle drivers will be aware of motorcycles in their vicinity: for example, by a Motorcycle Approach Warning.
Furthermore, C-ITS could enable information to the motorcycle rider about hazardous situations on the road ahead e.g. road works or broken-down vehicles.
This Cooperative Intelligent Transport System (C-ITS) has been initiated by car makers to improve driving safety. A promising technology to make sure, that other vehicle drivers will be aware of motorcycles in their vicinity: for example, by a Motorcycle Approach Warning.
Furthermore, C-ITS could enable information to the motorcycle rider about hazardous situations on the road ahead e.g. road works or broken-down vehicles.
However: Motorcycles are different.
Since motorcycles have different design and vehicle dynamics compared to cars, it is not possible to simply copy car systems and install them on motorcycles. Motorcycles, unlike cars, depend largely on active safety features; they have no crumble zones or brake assist facilities. But the vehicle dyamics are totally different from cars, e.g. steering is done by leaning in corners, not solely by a steering wheel. And not having a protective body means the technological layout has to be completely different as well. This way, many motorcycle-specific issues are to be resolved.
The role of CMC
CMC will investigate these key issues; Evaluation, verification and possibly standardization of basic requirements will be part of the focus of the consortium and laid down in a 'Basic Specification'.
CMC is not aiming at a particular communication technology, since CMC considers these basic requirements being technology open.
CMC is not aiming at a particular communication technology, since CMC considers these basic requirements being technology open.
Examples
Connectivity between vehicles allows to warn drivers about many scenario’s where there may be imminent danger. Many of such warnings are under development by the car industry. However, for motocycle specific situations, they should be adapted, or even newly developed.
The Connected Motorcycle Consortium is working on around 30 of these scenario's. A selection of these is described more in-depth on our Applications page.
Below are 6 videos to showcase specific examples:
Click the video to start
The Connected Motorcycle Consortium is working on around 30 of these scenario's. A selection of these is described more in-depth on our Applications page.
Below are 6 videos to showcase specific examples:
Click the video to start
Intersection Movement Assist |
Left Turn Assist |
Do No Pass Warning |
Road Works Warning |
Emergency Electronic Brake Light
|
Approaching Emergency Vehicle Warning |
The roadmap towards safety
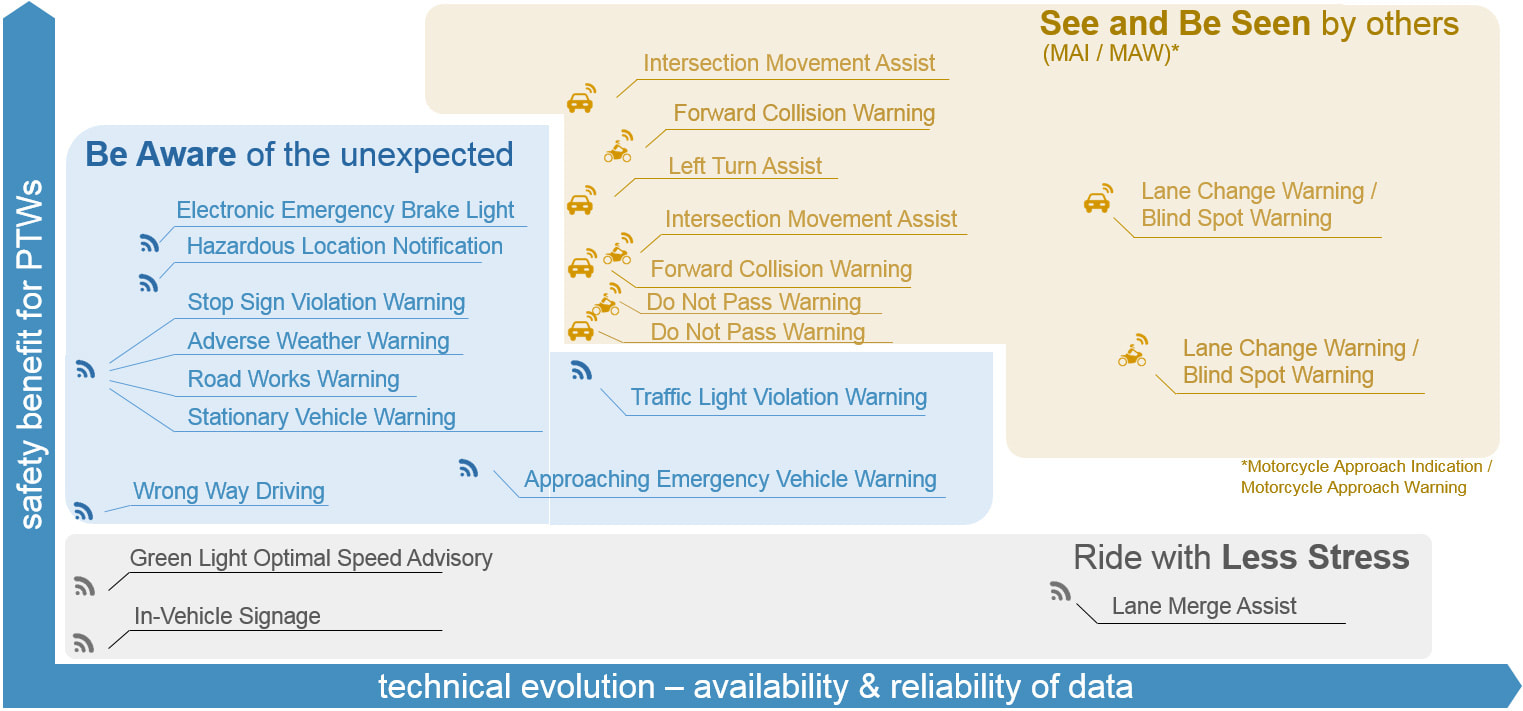
How to prioritise the applications to work on? CMC has developed a so-called roadmap that lays out all important safety applications.
In this map, the horizontal axis is a time scale that represents future technological developments and the vertical axis represents the potential impact an application has on motorcycle safety statistics.
Obviously, through time, the applications that have the highest impact on safety are the ones to be prioritised.
CMC has recently analysed an extensive German accident statistics database to evaluate 19 applications for their potential impact in such actual accident situations. As a result, a ranking of applications with highest safety potential could be established.
In the visual below, these are plotted schematically through time (through the phases of C-ITS technical evolution).
They can be summarised into three groups:
In this map, the horizontal axis is a time scale that represents future technological developments and the vertical axis represents the potential impact an application has on motorcycle safety statistics.
Obviously, through time, the applications that have the highest impact on safety are the ones to be prioritised.
CMC has recently analysed an extensive German accident statistics database to evaluate 19 applications for their potential impact in such actual accident situations. As a result, a ranking of applications with highest safety potential could be established.
In the visual below, these are plotted schematically through time (through the phases of C-ITS technical evolution).
They can be summarised into three groups:
- Applications that help the motorcyclists to ride with less stress;
- Applications that warn the motorcyclist of unexpected situations;
- Applications that help vehicle drivers to see and get seen by others (i.e. not to overlook each other).